首先我们为 Spring Security 专门建立一个 Spring 的配置文件,该文件就专门用来作为 Spring Security 的配置。使用 Spring Security 我们需要引入 Spring Security 的 NameSpace。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:security="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.1.xsd">
</beans>
Spring Security 命名空间的引入可以简化我们的开发,它涵盖了大部分 Spring Security 常用的功能。它的设计是基于框架内大范围的依赖的,可以被划分为以下几块。
- Web/Http 安全:这是最复杂的部分。通过建立 filter 和相关的 service bean 来实现框架的认证机制。当访问受保护的 URL 时会将用户引入登录界面或者是错误提示界面。
- 业务对象或者方法的安全:控制方法访问权限的。
- AuthenticationManager:处理来自于框架其他部分的认证请求。
- AccessDecisionManager:为 Web 或方法的安全提供访问决策。会注册一个默认的,但是我们也可以通过普通 bean 注册的方式使用自定义的 AccessDecisionManager。
- AuthenticationProvider:AuthenticationManager 是通过它来认证用户的。
- UserDetailsService:跟 AuthenticationProvider 关系密切,用来获取用户信息的。
引入了 Spring Security 的 NameSpace 之后我们就可以使用该命名空间下的元素来配置 Spring Security 了。首先我们来定义一个 http 元素,security 只是我们使用命名空间的一个前缀。http 元素是用于定义 Web 相关权限控制的。
<security:http auto-config="true">
<security:intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER"/>
</security:http>
如上定义中,intercept-url 定义了一个权限控制的规则。pattern 属性表示我们将对哪些 url 进行权限控制,其也可以是一个正则表达式,如上的写法表示我们将对所有的 URL 进行权限控制;access 属性表示在请求对应的 URL 时需要什么权限,默认配置时它应该是一个以逗号分隔的角色列表,请求的用户只需拥有其中的一个角色就能成功访问对应的 URL。这里的 “ROLE_USER” 表示请求的用户应当具有 ROLEUSER 角色。“ROLE ” 前缀是一个提示 Spring 使用基于角色的检查的标记。
有了权限控制的规则了后,接下来我们需要定义一个 AuthenticationManager 用于认证。我们先来看如下定义:
<security:authentication-manager>
<security:authentication-provider>
<security:user-service>
<security:user name="user" password="user" authorities="ROLE_USER"/>
<security:user name="admin" password="admin" authorities="ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN"/>
</security:user-service>
</security:authentication-provider>
</security:authentication-manager>
authentication-manager 元素指定了一个 AuthenticationManager,其需要一个 AuthenticationProvider(对应 authentication-provider 元素)来进行真正的认证,默认情况下 authentication-provider 对应一个 DaoAuthenticationProvider,其需要 UserDetailsService(对应 user-service 元素)来获取用户信息 UserDetails(对应 user 元素)。这里我们只是简单的使用 user 元素来定义用户,而实际应用中这些信息通常都是需要从数据库等地方获取的,这个将放到后续再讲。我们可以看到通过 user 元素我们可以指定 user 对应的用户名、密码和拥有的权限。user-service 还支持通过 properties 文件来指定用户信息,如:
<security:user-service properties="/WEB-INF/config/users.properties"/>
其中属性文件应遵循如下格式:
username=password,grantedAuthority[,grantedAuthority][,enabled|disabled]
所以,对应上面的配置文件,我们的 users.properties 文件的内容应该如下所示:
#username=password,grantedAuthority[,grantedAuthority][,enabled|disabled]
user=user,ROLE_USER
admin=admin,ROLE_USER,ROLE_ADMIN
至此,我们的 Spring Security 配置文件的配置就完成了。完整配置文件将如下所示。
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:security="http://www.springframework.org/schema/security"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.1.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security/spring-security-3.1.xsd">
<security:http auto-config="true">
<security:intercept-url pattern="/**" access="ROLE_USER"/>
</security:http>
<security:authentication-manager>
<security:authentication-provider>
<security:user-service>
<security:user name="user" password="user" authorities="ROLE_USER"/>
<security:user name="admin" password="admin" authorities="ROLE_USER, ROLE_ADMIN"/>
</security:user-service>
</security:authentication-provider>
</security:authentication-manager>
</beans>
之后我们告诉 Spring 加载这个配置文件。通常,我们可以在 web.xml 文件中通过 context-param 把它指定为 Spring 的初始配置文件,也可以在对应 Spring 的初始配置文件中引入它。这里我们采用前者。
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/config/applicationContext.xml,/WEB-INF/config/spring-security.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
Spring 的配置文件是通过对应的 ContextLoaderListener 来加载和初始化的,上述代码中的 applicationContext.xml 文件就是对应的 Spring 的配置文件,如果没有可以不用配置。接下来我们还需要在 web.xml 中定义一个 filter 用来拦截需要交给 Spring Security 处理的请求,需要注意的是该 filter 一定要定义在其它如 SpringMVC 等拦截请求之前。这里我们将拦截所有的请求,具体做法如下所示:
<filter>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>springSecurityFilterChain</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
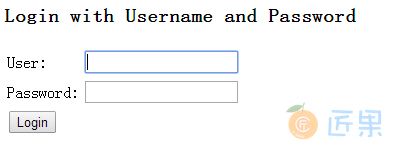
接下来可以启动我们的应用,然后在浏览器中访问我们的主页。你会看到如下页面。
因为我们的 Spring-security.xml 文件中配置好了所有的请求都需要 “ROLE_USER” 权限,所以当我们在请求主页的时候,Spring Security 发现我们还没有登录,Spring 会引导我们到登录界面。使用正确的用户名和密码(如上面配置的 user/user 或 admin/admin)登录后,如果符合对应的权限我们就可以访问主页了,否则将出现 403(禁止访问)界面。
可能你会奇怪,我们没有建立上面的登录页面,为什么 Spring Security 会跳到上面的登录页面呢?这是我们设置 http 的 auto-config=”true” 时 Spring Security 自动为我们生成的。
当指定 http 元素的 auto-config=”true” 时,就相当于如下内容的简写。
<security:http>
<security:form-login/>
<security:http-basic/>
<security:logout/>
</security:http>
这些元素负责建立表单登录、基本的认证和登出处理。它们都可以通过指定对应的属性来改变它们的行为。