- 首页
- 作品
- 运维笔记
- Linux 运维必备的 13 款实用工具
Linux 运维必备的 13 款实用工具
本文介绍几款 Linux 运维的实用的工具。
1、查看进程占用带宽情况-Nethogs
2、硬盘读取性能测试-IOZone
3、实时监控磁盘IO-IOTop
- IOTop命令是专门显示硬盘IO的命令,界面风格类似top命令。
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install iotop
4、网络流量监控-IPtraf
- IPtraf是一个运行在Linux下的简单的网络状况分析工具。
[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install iptraf
5、网络流量监控-IFTop
6、进程实时监控-HTop
- HTop是一个 Linux 下的交互式的进程浏览器可以用来替换Linux下的top命令。
rpm -ivh http://pkgs.repoforge.org/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.2-2.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm(安装第三方YUM源)[root@localhost ~]# yum -y install htop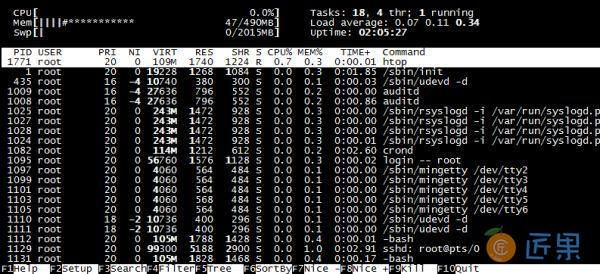
7、系统资源监控-NMON
8、监控多个日志-MultiTail
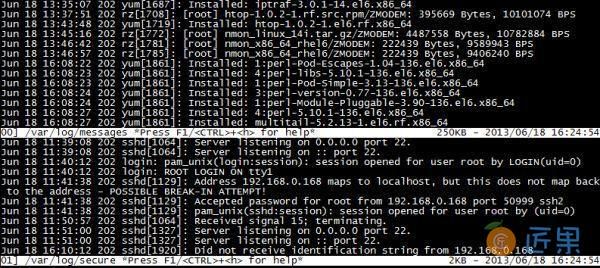
9、SSH暴力破解防护-Fail2ban
- Fail2ban可以监视你的系统日志然后匹配日志的错误信息正则式匹配执行相应的屏蔽动作一般情况下是调用防火墙屏蔽
- 下载地址:http://www.fail2ban.org/wiki/index.php/Downloads
-
[root@localhost ~]# cd fail2ban-0.8.11
[root@localhost fail2ban-0.8.11]# python setup.py install
[root@localhost fail2ban-0.8.11]# cd files/
[root@localhost files]# cp ./redhat-initd /etc/init.d/fail2ban
[root@localhost files]# service fail2ban start
[root@localhost files]# chkconfig --add fail2ban
[root@localhost files]# chkconfig fail2ban on
- 注:需要配置iptables实用,如果重启iptables了也要重启fail2ban,因为fail2ban的原理是调用iptables实时阻挡外界的攻击。
-
[root@localhost ~]# grep -v "^#" /etc/fail2ban/jail.conf | grep -v "^$" [DEFAULT]
ignoreip = 127.0.0.1/8#忽略本机IP
bantime = 600 #符合规则后封锁时间
findtime = 600 #在多长时间内符合规则执行封锁如600秒达到3次则执行
maxretry = 3 #最大尝试次数
backend = auto #日志修改检测日志gamin、polling和auto这三种
usedns = warn [ssh-iptables]
enabled = true#默认是禁用
false filter = sshd action = iptables[name=SSH, port=ssh, protocol=tcp] # sendmail-whois[name=SSH,dest=收件人邮箱, sender=发件人邮箱, sendername="Fail2Ban"] logpath = /var/log/sshd.log #响应的错误日志一般在/var/log/secure maxretry = 5 #尝试错误次数覆盖全局中的maxretry
- 注:默认所有的应用防护都是关闭的,需要我们手动开启。fail2ban.conf文件是日志信息,jail.conf文件是保护的具体服务和动作配置信息。
-
[root@localhost ~]# touch /var/log/sshd.log
[root@localhost ~]# service fail2ban restart
[root@localhost ~]# fail2ban-client status #查看监控已经开启 Status |- Number of jail: 1 `- Jail list: ssh-iptables
[root@localhost ~]# iptables -L #iptables过滤表有fail2ban一条规则 fail2ban-SSH tcp -- anywhere anywhere tcp dpt:ssh
10、连接会话终端持续化-Tmux
- Tmux是一个优秀的终端复用软件类似GNU Screen比Screen更加方面、灵活和高效。为了确保连接SSH时掉线不影响任务运行。
rpm -ivh http://pkgs.repoforge.org/rpmforge-release/rpmforge-release-0.5.2-2.el6.rf.x86_64.rpm(安装第三方YUM源)
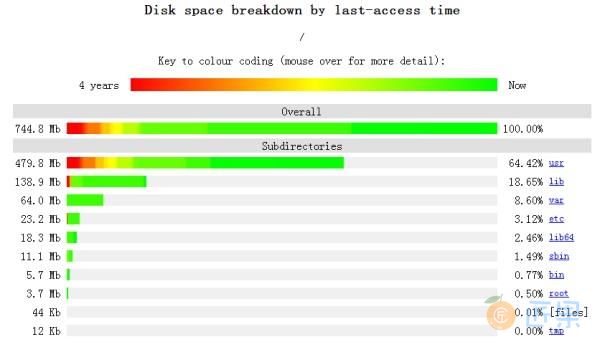
11、页面显示磁盘空间使用情况-Agedu
12、安全扫描工具-NMap
13、Web压力测试-Httperf
- Httperf比ab更强大,能测试出Web服务能承载的最大服务量及发现潜在问题;比如:内存使用、稳定性。最大优势:可以指定规律进行压力测试,模拟真实环境。
- 下载地址:http://code.google.com/p/httperf/downloads/list
-
[root@localhost ~]# tar zxvf httperf-0.9.0.tar.gz
[root@localhost ~]# cd httperf-0.9.0
[root@localhost httperf-0.9.0]# ./configure
[root@localhost httperf-0.9.0]# make && make install
[root@localhost ~]# httperf --hog --server=192.168.0.202 --uri=/index.html --num-conns=10000 --wsess=10,10,0.1
下一节:因为网络传输的限制,很多时候,我们需要在 Linux 系统下对大文件进行切割。将一个大文件切割成为多个小文件,当传输完毕之后再进行合并。这样做的好处是效率更高。