依赖管理是技术栈的重要一环,几乎所有的现代编程语言都拥有自己的依赖管理系统。
如果你在很久以前就从事了Java开发,或者参与过一些"不太正规"的项目,一定经历有过"jar包随便拷、jar包满天飞"的经历。在这种情况下,每次上线发布、升级jar包都是非常痛苦的事情。
大概从2003年开始,构建工具逐渐走入Java开发者的视野,Maven是构建工具中应用最为广泛的工具之一,它在提供构建功能的同时,也自带了强大的依赖管理功能。采用maven后,我们只需要定义XML就可以自动下载依赖的jar包,而不需要"手动将jar包拷来拷去"。
近几年来,作为一种更高效的构建工具 - Gradle - 逐渐崛起,在一些开发领域(如Android),Gradle已经完全取代了Maven成为事实上的构建标准。
尽管从构建工具的角度而言,Maven的地位有所下降,但它在Java依赖管理子领域的地位却不容撼动。Gradle默认也是直接采取Maven的依赖管理框架(只不过换为更简便的描述语言)。
在 架构概览 一章中,我们已经说明:在选型上,我们使用Gradle作为构建工具,但依然采用Maven来管理依赖。
在Maven的依赖管理方面,我们将使用Nexus搭建私有Maven服务器。为什么要搭建私服呢?
这和为什么搭建私有Git服务器却不用GitHub公开仓库是一个道理:没有公司愿意将自己的代码暴露给全世界:-)
Nexus仓库的基本配置
与前两节类似,我们首先在Kubernetes上部署Nexus服务。创建之前,先在物理机上创建Volume挂载点:
minikube ssh
$sudo mkdir /data/nexus
$sudo chmod -R 777 /data/nexus/
这里因为nexus需要有一个文件锁,默认权限是不够的,我们给了777权限,如果你觉得过于宽松,可以自行更改Kubernetes的启动用户,并设定相应权限。
看一下部署文件, nexus-deployment.yaml:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nexus-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nexus
replicas: 1
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nexus
spec:
restartPolicy: Always
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/hostname: minikube
containers:
- name: nexus-ct
image: sonatype/nexus:2.14.8
ports:
- containerPort: 8081
hostPort: 8081
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: "/sonatype-work"
name: volume
volumes:
- name: volume
hostPath:
path: /data/nexus/
部署一下:
kubectl apply -f ./nexus-deployment.yaml
一切顺利的话,稍等一会访问"http://192.168.99.100:8081/nexus:
Nexus接入LDAP帐号
服务虽然好了,但还没有接入LDAP帐号系统,Nexus中接入LDAP帐号较为繁琐,请耐心操作完。
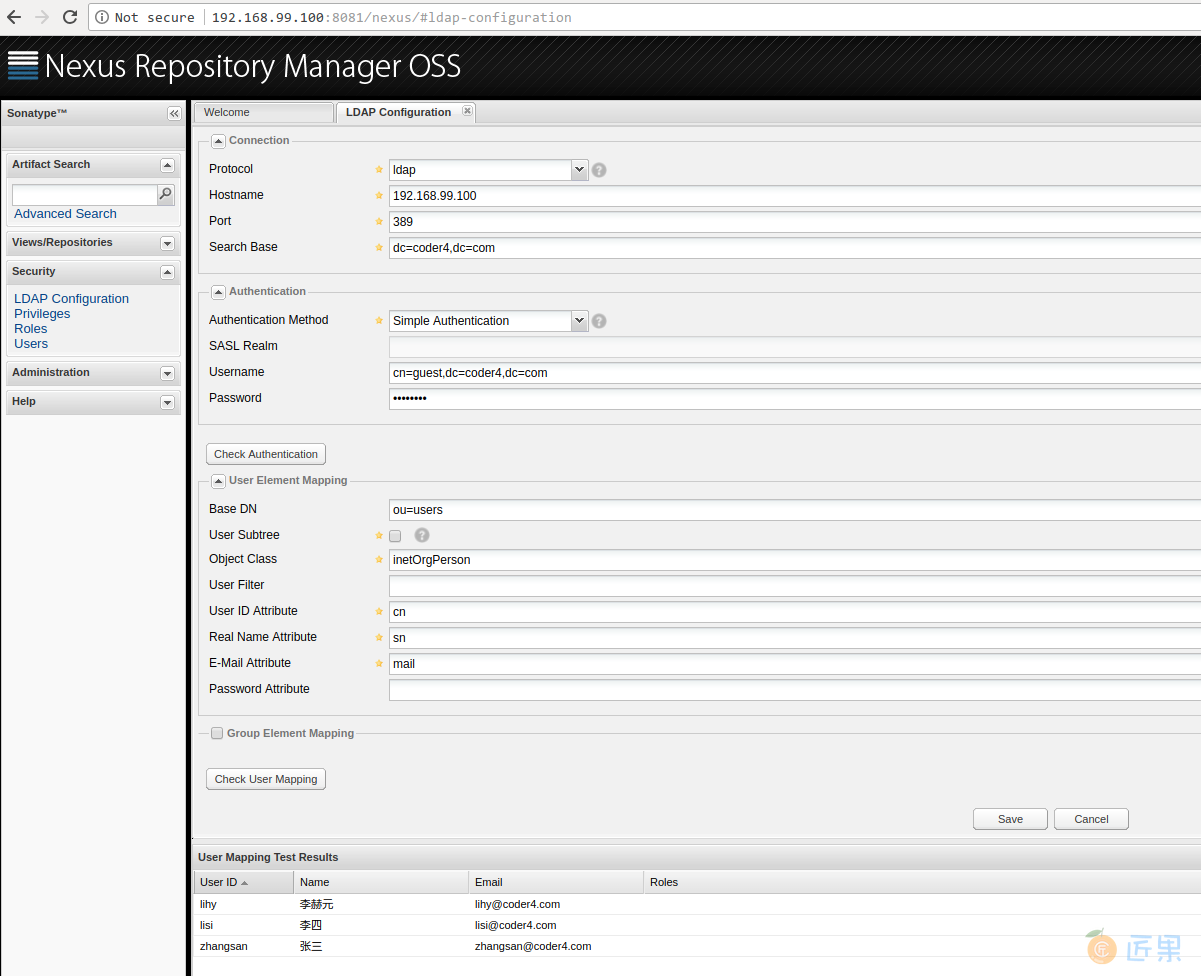
首先,设置一下LDAP的连接配置。
- 使用默认管理员帐号登录,用户名admin,密码admin123
- 点击左侧菜单"Security" -> "LDAP Configuration"
- 设置LDAP配置如下
- Protocol: ldap
- Hostname: 192.168.99.100
- SearchBase: dc=coder4,dc=com
- Authentication Method: Simple Authentication
- Username: cn=guest,dc=coder4,dc=com
- Password: guest123
- Base DN: ou=users
- Object Class: inetOrgPerson
- User ID Attribute: cn
- Real Name Attribute: sn
- E-Mail Attribute: mail
- Group Element Mapping: 不选中
上述配置稍显繁琐,请耐心完成。都配置完成后,点击"Save"。
此外,点击底部的"Check User Mapping",如果一切配置正确,可以展示所有的列表,如下图所示。
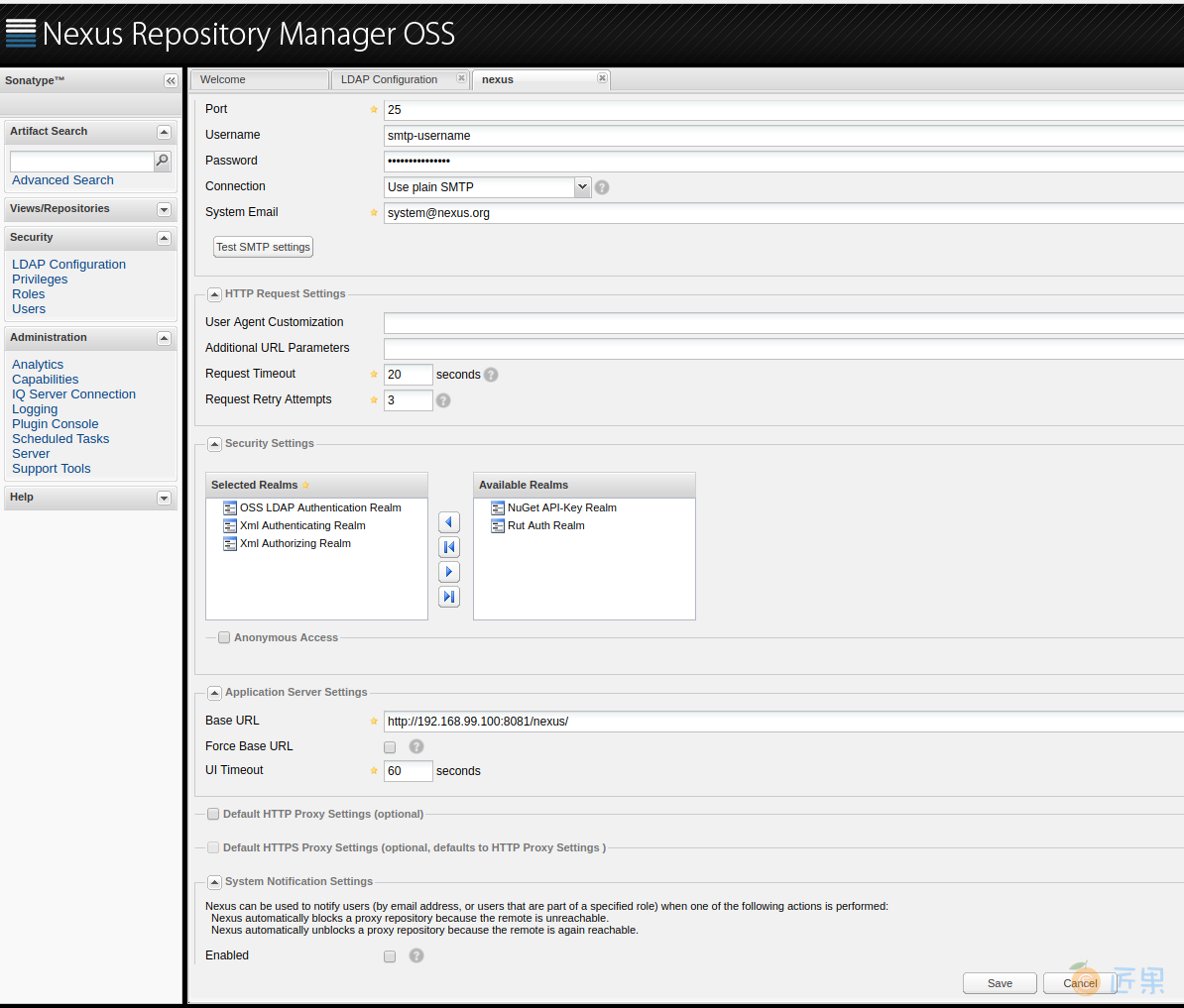
第二步,下面我们来更改默认认证方式为LDAP。
点击左侧菜单"Administration" -> "Server",进行如下配置:
- 在Security Settings中,将右侧的"OSS LDAP Authentication Realm"加入到左边,并将其拖动到最顶部。
- 取消勾选"Anoymous Access"。
配置可以参考上图,设置好后,点击"Save"。
最后,我们需要对所有用户配置权限,注意,每次LDAP新接入用户后,都要执行下述操作。
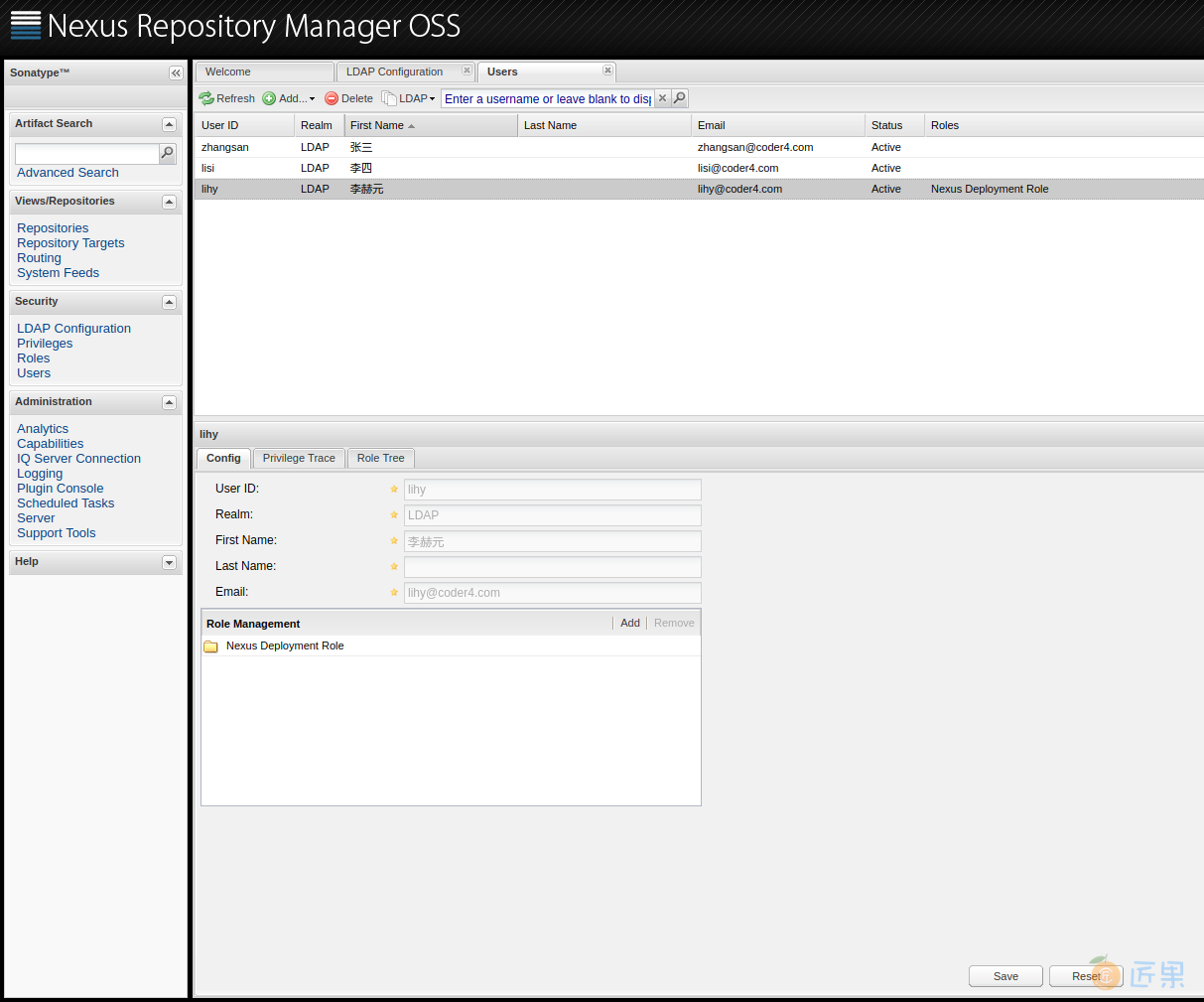
点击左侧菜单"Security" -> "Users" ,执行下述操作:
- 点击"All Configured Users"旁边的小箭头,选择"LDAP"
- 点击"Refresh",此时就能拿到所有LDAP中的用户了。
- 选中一个要操作的用户,例如"lihy",选择底部的"Config",然后"Role Management"。
- 一般用户给"Nexus Deployment Role"就可以了,管理员可以给"Nexus Administrator Role"。
- 设置好后点击"Save"
一个配置好的结果如上图所示。
至此,我们已经成功接入了LDAP,试着用配置好的用户登录下,发现可以登录成功。
配置Nexus中央仓库的缓存
Maven依赖仓库也是分布式,我们最长用的,是"Maven Central"这个中央仓库。
我们建议将中央仓库的索引缓存到Nexus私服上,这大约需要20GB的空间。
使用管理员帐号登录后,点击左侧菜单"View/Repositories":
- 选择"Repositories"
- 在右侧选择"Central"这个仓库
- 底部"Configuration"配置
- Remote Storage Location: http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/repositories/central/ (这里我们使用了阿里云的国内镜像以加快速度)
- Download Remote Indexes: True
- 最后点击底部的"Save"
缓存的时间比较长,在我的虚拟机上,花费了20分钟。进度可以在这里查看,左侧菜单"Administration" -> "Logging" 选择Log, 可以看到目前还在缓存:
2018-05-28 08:40:19,792+0000 INFO [pxpool-1-thread-1] admin org.sonatype.nexus.index.DefaultIndexerManager - Trying to get remote index for repository "Central" [id=central]
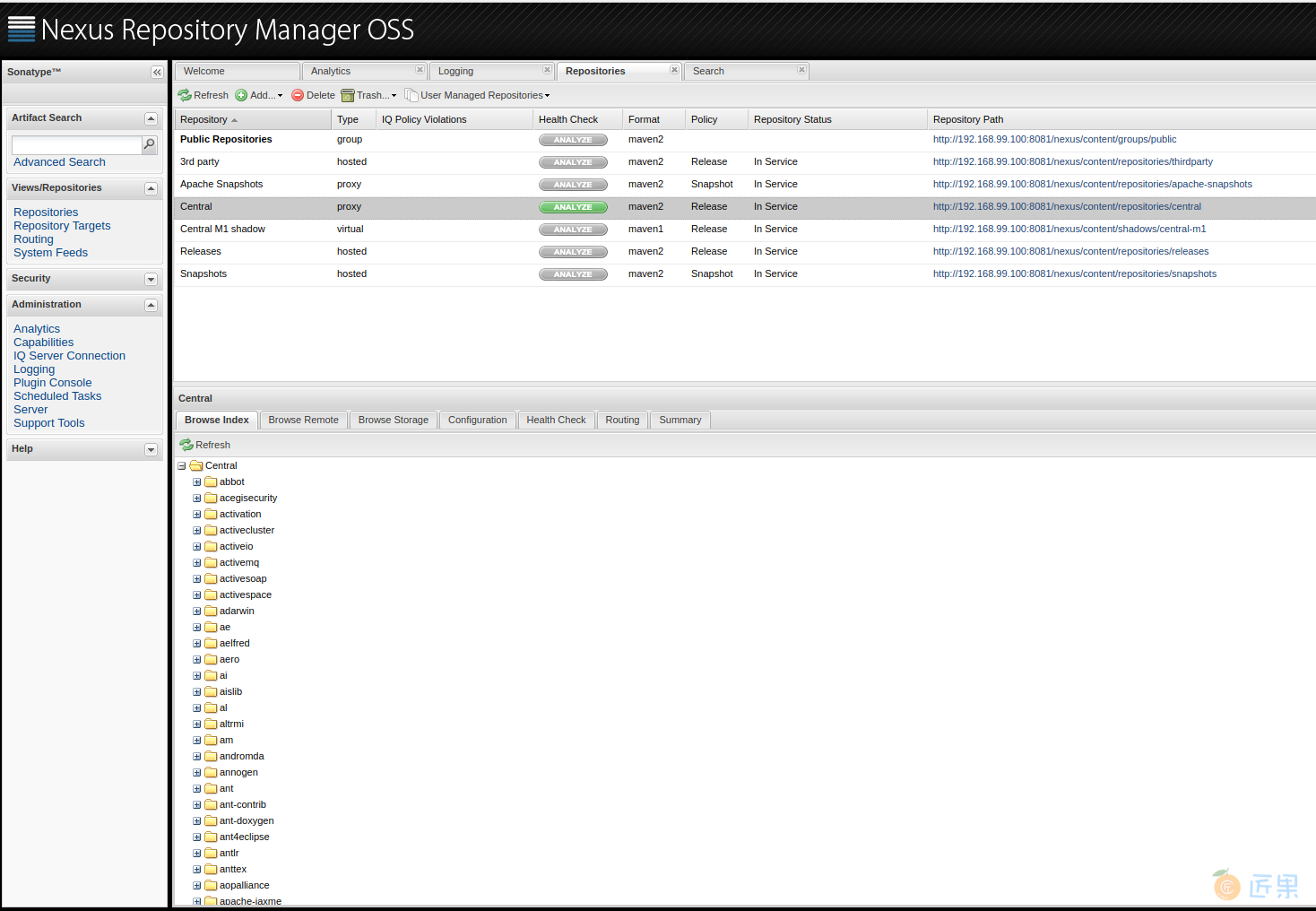
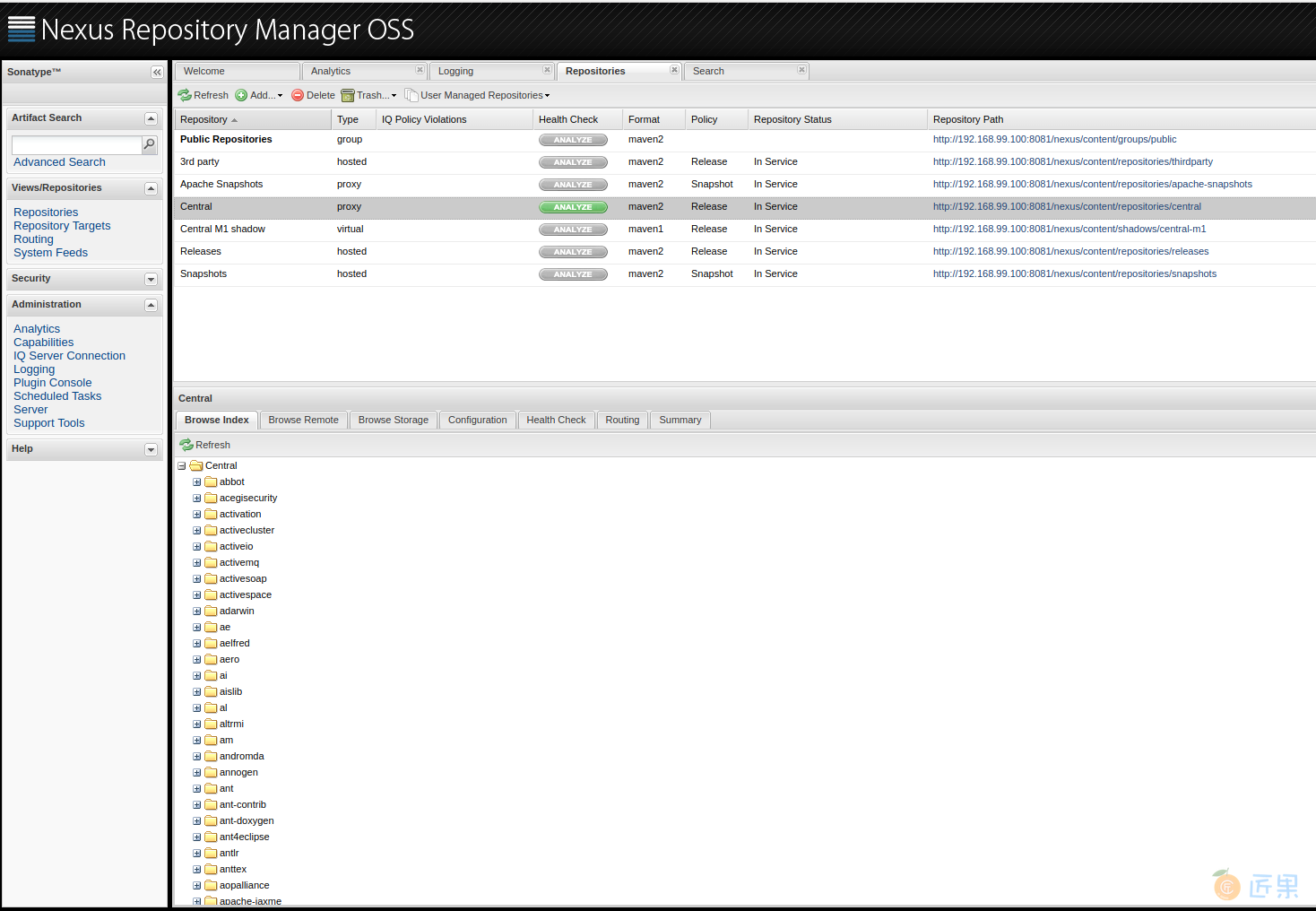
等缓存成功后,在本地仓库的"Browse Index中",应当能看到与中央仓库一样的目录结构,如下图所示:
至此,我们成功架设了基于Nexus的Maven私有仓库,集成了LDAP登录,并缓存了Maven中央仓库。
如何在Gradle中应用私有仓库
在配置了私有仓库后,我们还需要在微服务项目中启用这个私有仓库。
这大致需要2步
- 配置maven私有仓库用户名和密码
- build.gradle中配置
下面我们分别看一下
配置Maven私有仓库用户名和米按摩
vim ~/.m2/settings.xml
# 新增如下内容
<settings>
<servers>
<server>
<id>nexus_coder4</id>
<username>lihy</username>
<password>pass</password>
</server>
</servers>
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<!--This sends everything else to /public -->
<id>nexus_coder4</id>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
<url>http://192.168.99.100:8081/content/groups/public</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>nexus_coder4</id>
<!--Enable snapshots for the built in central repo to direct -->
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>central</id>
<url>http://192.168.99.100:8081/content/groups/public</url>
<releases><enabled>true</enabled></releases>
<snapshots><enabled>true</enabled></snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>central</id>
<url>http://192.168.99.100:8081/content/groups/public</url>
<releases><enabled>true</enabled></releases>
<snapshots><enabled>true</enabled></snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</profile>
</profiles>
<activeProfiles>
<activeProfile>nexus_coder4</activeProfile>
</activeProfiles>
</settings>
如上,我们新增了私有仓库的地址、用户配置,如果你觉得在文件中直接"裸写"密码不安全,可以参考maven密码加密方法。
下面,我们在build.gradle中配置:
buildscript {
repositories {
maven { url 'http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public' }
maven { url 'https://jitpack.io' }
}
dependencies {
// version just for plugin, not important
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:1.5.6.RELEASE")
}
}
subprojects {
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'idea'
apply plugin: 'maven'
apply plugin: 'org.springframework.boot'
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
targetCompatibility = 1.8
group = 'com.coder4.lmsia'
version = '0.0.1'
repositories {
maven {
credentials {
username "$mavenUser"
password "$mavenPass"
}
url 'http://192.168.99.100:8081/nexus/content/groups/public'
}
mavenLocal()
}
// maven deploy config start
configurations {
deployerJars
}
uploadArchives {
repositories.mavenDeployer {
configuration = configurations.deployerJars
repository(url: "http://192.168.99.100:8081/nexus/content/repositories/releases/") {
authentication(userName: "$mavenUser", password: "$mavenPass")
}
snapshotRepository(url: "http://192.168.99.100:8081/nexus/content/repositories/snapshots/") {
authentication(userName: "$mavenUser", password: "$mavenPass")
}
}
}
// maven deploy config end
}
如上,build.gradle主要进行如下配置:
- 子项目的仓库,采用私有仓库
- 子项目发布包时,也发布到私有仓库上
至此,我们成功地将maven私有仓库应用到了gradle的微服务上。
下一节:在应用了Gradle构建工具,以及Maven仓库来管理版本依赖后,程序的构建、依赖问题已经得到了基本的解决。但随着项目的不断发展,一个微服务的依赖可能会越来越多,出现版本冲突的问题。