Python从2.5版本开始引入了 with 语法。此语法非常实用,在有两个相关的操作需要在一部分代码块前后分别执行的时候,可以使用 with 语法自动完成。同事,使用 with语法可以在特定的地方分配和释放资源,因此,with语法也叫做“上下文管理器”。在threading模块中,所有带有acquire()方法和release() 方法的对象都可以使用上下文管理器。
也就是说,下面的对象可以使用 with 语法:
- Lock
- RLock
- Condition
- Semaphore
1. 准备工作
在本节中,我们将使用 with 语法简单地尝试这四个对象。
2. 如何做…
下面的例子展示了 with 语法的基本用法,我们有一系列的同步原语,下面尝试用 with 来使用它们:
import threading
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, format='(%(threadName)-10s) %(message)s',)
def threading_with(statement):
with statement:
logging.debug('%s acquired via with' % statement)
def threading_not_with(statement):
statement.acquire()
try:
logging.debug('%s acquired directly' % statement )
finally:
statement.release()
if __name__ == '__main__':
# let's create a test battery
lock = threading.Lock()
rlock = threading.RLock()
condition = threading.Condition()
mutex = threading.Semaphore(1)
threading_synchronization_list = [lock, rlock, condition, mutex]
# in the for cycle we call the threading_with e threading_no_with function
for statement in threading_synchronization_list :
t1 = threading.Thread(target=threading_with, args=(statement,))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=threading_not_with, args=(statement,))
t1.start()
t2.start()
t1.join()
t2.join()
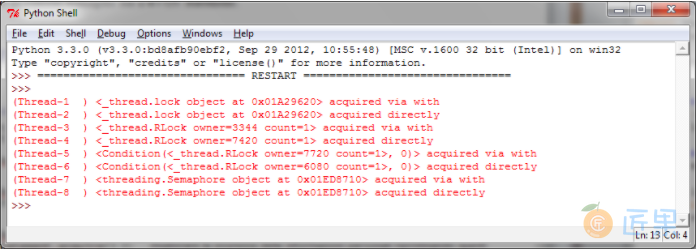
下图展示了使用 with 的每一个函数以及用在了什么地方:
3. 讨论
在主程序中,我们定义了一个list, threading_synchronization_list ,包含要测试的线程同步使用的对象:
lock = threading.Lock()
rlock = threading.RLock()
condition = threading.Condition()
mutex = threading.Semaphore(1)
threading_synchronization_list = [lock, rlock, condition, mutex]
定义之后,我们可以在 for 循环中测试每一个对象:
for statement in threading_synchronization_list :
t1 = threading.Thread(target=threading_with, args=(statement,))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=threading_not_with, args=(statement,))
最后,我们有两个目标函数,其中 threading_with 测试了 with 语法:
def threading_with(statement):
with statement:
logging.debug('%s acquired via with' % statement)
4. 了解更多
在本例中,我们使用了Python的logging模块进行输出:
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG, format='(%(threadName)-10s) %(message)s',)
使用 % (threadName) 可以在每次输出的信息都加上线程的名字。logging模块是线程安全的。这样我们可以区分出不同线程的输出。
译者注:译者在博客上写过一篇有关Python的with语句的文章,可以参考一下:https://www.kawabangga.com/posts/2010